
[ad_1]
One of many oldest malware tips within the e-book — hacked web sites claiming guests have to replace their Internet browser earlier than they’ll view any content material — has roared again to life prior to now few months. New analysis exhibits the attackers behind one such scheme have developed an ingenious manner of preserving their malware from being taken down by safety consultants or legislation enforcement: By internet hosting the malicious recordsdata on a decentralized, nameless cryptocurrency blockchain.
In August 2023, safety researcher Randy McEoin blogged a few rip-off he dubbed ClearFake, which makes use of hacked WordPress websites to serve guests with a web page that claims it is advisable to replace your browser earlier than you’ll be able to view the content material.
The pretend browser alerts are particular to the browser you’re utilizing, so if you happen to’re browsing the Internet with Chrome, for instance, you’ll get a Chrome replace immediate. Those that are fooled into clicking the replace button can have a malicious file dropped on their system that tries to put in an info stealing trojan.
Earlier this month, researchers on the Tel Aviv-based safety agency Guardio mentioned they tracked an up to date model of the ClearFake rip-off that included an essential evolution. Beforehand, the group had saved its malicious replace recordsdata on Cloudflare, Guardio mentioned.
However when Cloudflare blocked these accounts the attackers started storing their malicious recordsdata as cryptocurrency transactions within the Binance Good Chain (BSC), a know-how designed to run decentralized apps and “good contracts,” or coded agreements that execute actions robotically when sure situations are met.
Nati Tal, head of safety at Guardio Labs, the analysis unit at Guardio, mentioned the malicious scripts stitched into hacked WordPress websites will create a brand new good contract on the BSC Blockchain, beginning with a singular, attacker-controlled blockchain tackle and a set of directions that defines the contract’s capabilities and construction. When that contract is queried by a compromised web site, it’ll return an obfuscated and malicious payload.
“These contracts supply modern methods to construct functions and processes,” Tal wrote alongside along with his Guardio colleague Oleg Zaytsev. “As a result of publicly accessible and unchangeable nature of the blockchain, code might be hosted ‘on-chain’ with out the flexibility for a takedown.”
Tal mentioned internet hosting malicious recordsdata on the Binance Good Chain is right for attackers as a result of retrieving the malicious contract is a cost-free operation that was initially designed for the aim of debugging contract execution points with none real-world affect.
“So that you get a free, untracked, and sturdy option to get your knowledge (the malicious payload) with out leaving traces,” Tal mentioned.
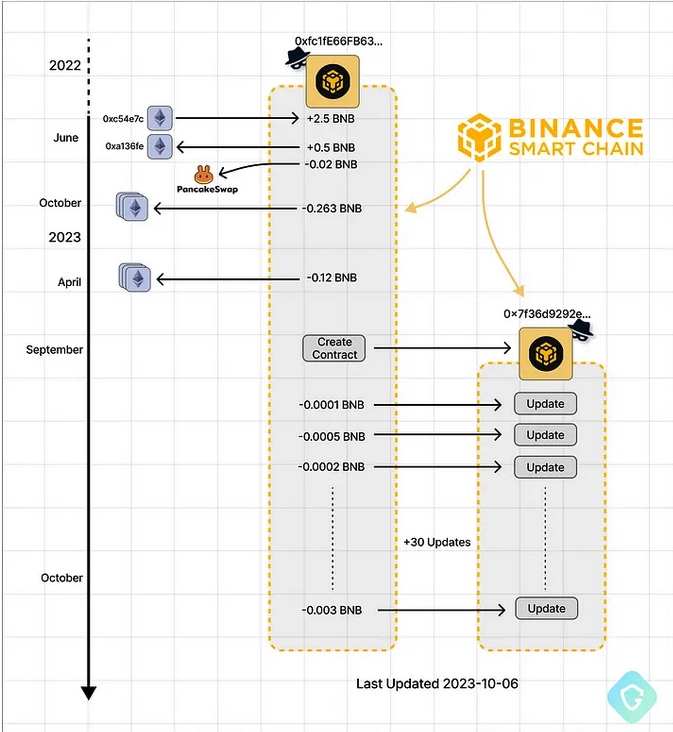
Attacker-controlled BSC addresses — from funding, contract creation, and ongoing code updates. Picture: Guardio
In response to questions from KrebsOnSecurity, the BNB Good Chain (BSC) mentioned its crew is conscious of the malware abusing its blockchain, and is actively addressing the problem. The corporate mentioned all addresses related to the unfold of the malware have been blacklisted, and that its technicians had developed a mannequin to detect future good contracts that use comparable strategies to host malicious scripts.
“This mannequin is designed to proactively establish and mitigate potential threats earlier than they’ll trigger hurt,” BNB Good Chain wrote. “The crew is dedicated to ongoing monitoring of addresses which might be concerned in spreading malware scripts on the BSC. To reinforce their efforts, the tech crew is engaged on linking recognized addresses that unfold malicious scripts to centralized KYC [Know Your Customer] info, when potential.”
Guardio says the crooks behind the BSC malware scheme are utilizing the identical malicious code because the attackers that McEoin wrote about in August, and are possible the identical group. However a report revealed right this moment by e mail safety agency Proofpoint says the corporate is presently monitoring at the least 4 distinct risk actor teams that use pretend browser updates to distribute malware.
Proofpoint notes that the core group behind the pretend browser replace scheme has been utilizing this system to unfold malware for the previous 5 years, primarily as a result of the strategy nonetheless works nicely.
“Pretend browser replace lures are efficient as a result of risk actors are utilizing an end-user’s safety coaching in opposition to them,” Proofpoint’s Dusty Miller wrote. “In safety consciousness coaching, customers are instructed to solely settle for updates or click on on hyperlinks from recognized and trusted websites, or people, and to confirm websites are legit. The pretend browser updates abuse this coaching as a result of they compromise trusted websites and use JavaScript requests to quietly make checks within the background and overwrite the present web site with a browser replace lure. To an finish consumer, it nonetheless seems to be the identical web site they had been intending to go to and is now asking them to replace their browser.”
Greater than a decade in the past, this web site revealed Krebs’s Three Guidelines for On-line Security, of which Rule #1 was, “For those who didn’t go on the lookout for it, don’t set up it.” It’s good to know that this technology-agnostic strategy to on-line security stays simply as related right this moment.
[ad_2]