
[ad_1]
(Nanowerk Information) There are numerous creatures on our planet with extra superior senses than people. Turtles can sense Earth’s magnetic area. Mantis shrimp can detect polarized gentle. Elephants can hear a lot decrease frequencies than people can. Butterflies can understand a broader vary of colours, together with ultraviolet (UV) gentle.
Key Takeaways

The Analysis
The Imitation Recreation
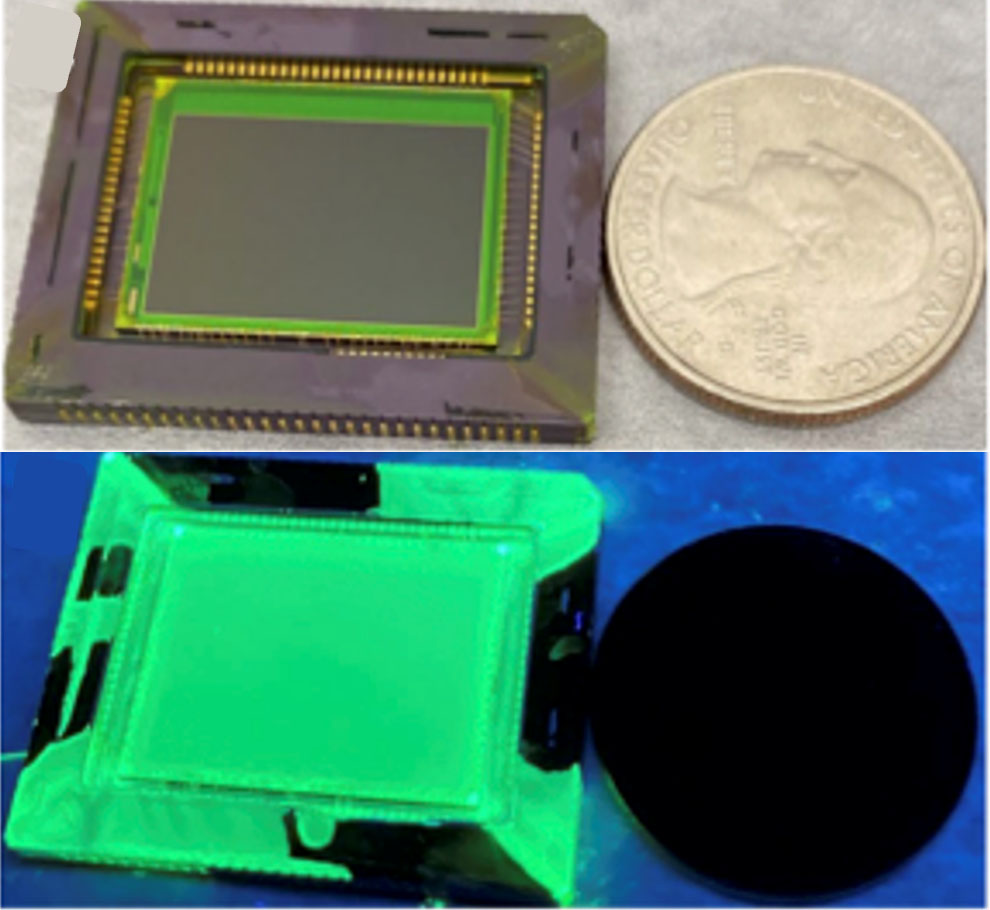
Healthcare and Past
[ad_2]