[ad_1]
A set of novel assault strategies has been demonstrated in opposition to Google Workspace and the Google Cloud Platform that might be probably leveraged by risk actors to conduct ransomware, information exfiltration, and password restoration assaults.
“Ranging from a single compromised machine, risk actors may progress in a number of methods: they may transfer to different cloned machines with GCPW put in, acquire entry to the cloud platform with customized permissions, or decrypt domestically saved passwords to proceed their assault past the Google ecosystem,” Martin Zugec, technical options director at Bitdefender, stated in a brand new report.
A prerequisite for these assaults is that the unhealthy actor has already gained entry to a neighborhood machine by way of different means, prompting Google to mark the bug as not eligible for fixing “because it’s exterior of our risk mannequin and the conduct is according to Chrome’s practices of storing native information.”
Nevertheless, the Romanian cybersecurity agency has warned that risk actors can exploit such gaps to increase a single endpoint compromise to a network-wide breach.
The assaults, in a nutshell, depend on a company’s use of Google Credential Supplier for Home windows (GCPW), which affords each cell gadget administration (MDM) and single sign-on (SSO) capabilities.
This allows directors to remotely handle and management Home windows gadgets inside their Google Workspace environments, in addition to permits customers to entry their Home windows gadgets utilizing the identical credentials which might be used to login to their Google accounts.
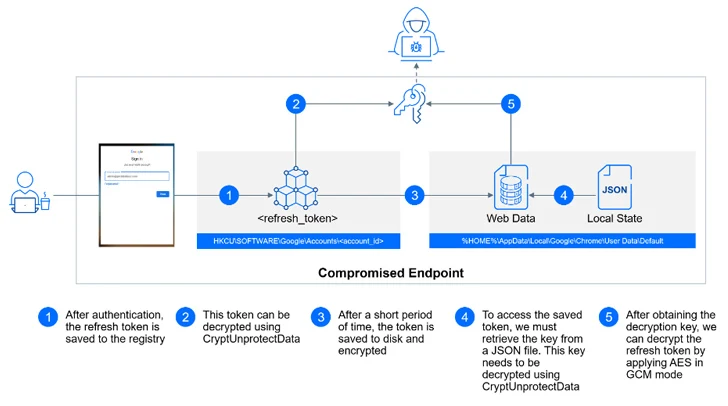
GCPW is designed to make use of a neighborhood privileged service account named Google Accounts and ID Administration (GAIA) to seamlessly facilitate the method within the background by connecting to Google APIs for verifying a person’s credentials throughout the sign-in step and storing a refresh token to obviate the necessity for re-authentication.
With this setup in place, an attacker with entry to a compromised machine can extract an account’s refresh OAuth tokens, both from the Home windows registry or from the person’s Chrome profile listing, and bypass multi-factor authentication (MFA) protections.
The refresh token is subsequently utilized to assemble an HTTP POST request to the endpoint “https://www.googleapis[.]com/oauth2/v4/token” to acquire an entry token, which, in flip, might be abused to retrieve, manipulate, or delete delicate information related to the Google Account.
A second exploit considerations what’s referred to as the Golden Picture lateral motion, which focuses on digital machine (VM) deployments and takes benefit of the truth that making a machine by cloning one other machine with pre-installed GCPW causes the password related to the GAIA account to be cloned as effectively.
“If you understand the password to a neighborhood account, and native accounts on all machines share the identical password, then you understand the passwords to all machines,” Zugec defined.
“This shared-password problem is much like having the identical native administrator password on all machines that has been addressed by Microsoft’s Native Administrator Password Resolution (LAPS).”
The third assault entails entry to plaintext credentials by leveraging the entry token acquired utilizing the aforementioned method to ship an HTTP GET request to an undocumented API endpoint and pay money for the non-public RSA key that’s required to decrypt the password discipline.
“Getting access to plaintext credentials, equivalent to usernames and passwords, represents a extra extreme risk,” Zugec stated. “It’s because it permits attackers to instantly impersonate official customers and acquire unrestricted entry to their accounts, probably main to finish account takeover.”
[ad_2]