
[ad_1]
In an period of fast digital transformation, we now have witnessed a regarding evolution within the cyber risk panorama. Latest information analyses, as illustrated within the “Cyber Risk Intelligence Index: Q3 2023” report, underscore the escalating complexity and prevalence of cyber vulnerabilities and malware sorts.
The dominance of malware households like CobaltStrike and SmokeLoader, mixed with the intensive use of techniques similar to Command and Management and Protection Evasion, signifies a classy and stealthy strategy by cyber adversaries. Moreover, the sharp improve within the variety of vulnerabilities, particularly these which can be publicly exploitable or with out a identified answer, paints a grim image for cyber defenders.
As we step into 2024, there’s a palpable apprehension surrounding the realm of cyber threats. The interconnected nature of in the present day’s world, bolstered by the Web of Issues (IoT) and intensive digital integration, has broadened the assault floor for malicious actors. It’s not simply massive companies or governments which can be in danger; on a regular basis customers, small companies, and very important infrastructure parts have discovered themselves within the crosshairs of those cyber onslaughts. The tangible results of such assaults can vary from monetary losses and information breaches to the crippling of important companies and the erosion of public belief in digital methods.
The statistics from the third quarter of 2023 function a stark reminder that complacency is now not an choice. The shifting dynamics of malware sorts, with Trojans and Distant Entry Trojans main the cost, spotlight the significance of proactive protection and staying forward of the risk curve. As ransomware, although constituting a smaller share, continues to wreak havoc with its high-impact assaults, the urgency to prioritize cybersecurity has by no means been clearer.
The rising concern of cyber-attacks should not simply based mostly on numbers however on the evolving sophistication, scale, and potential ramifications of those threats. Now, greater than ever, there’s a collective name to motion for people, companies, and governments alike to fortify their cyber defenses, spend money on analysis and coaching, and foster collaboration to counter these looming digital risks.
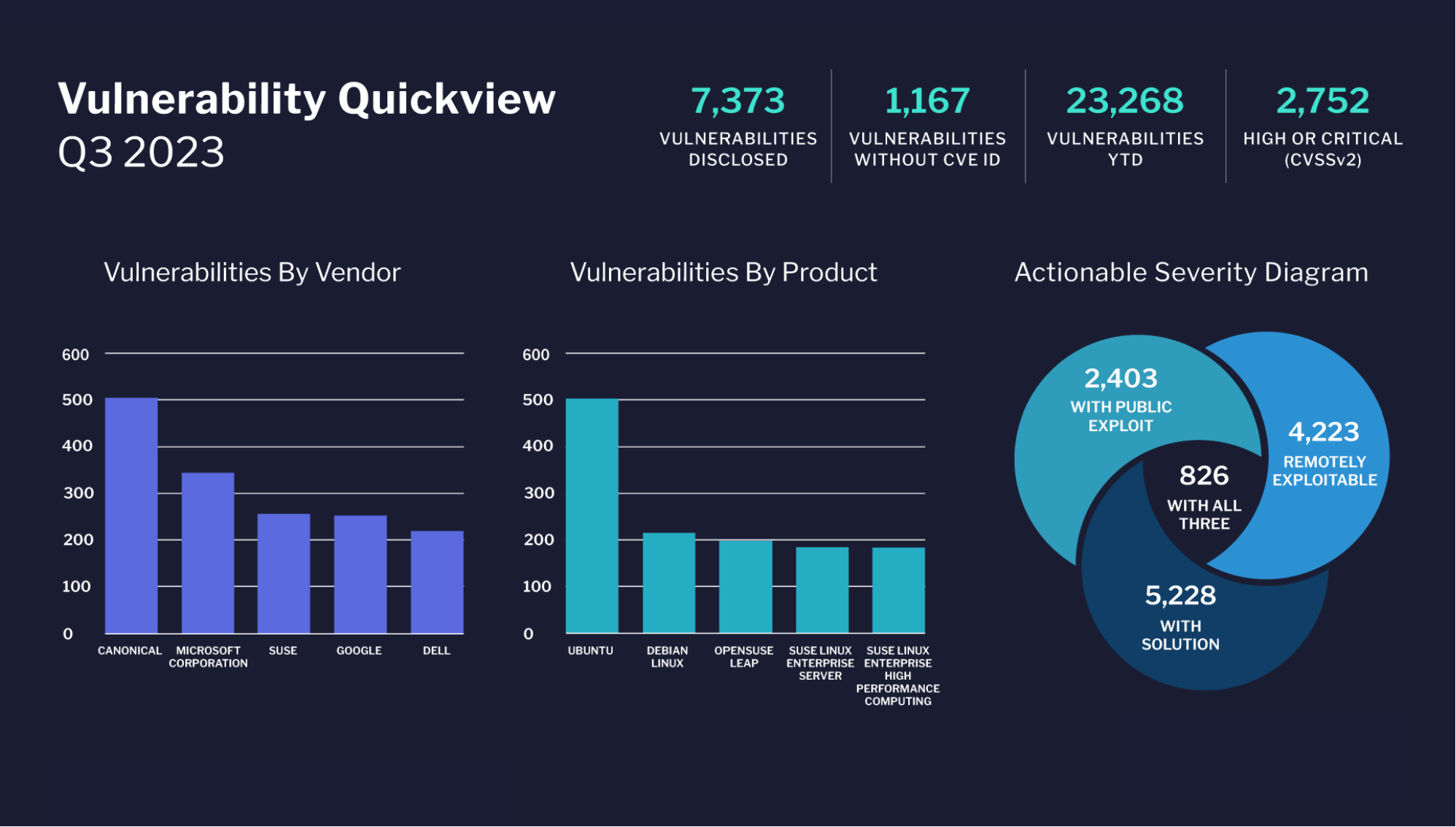
Vulnerability Quickview
The graphic offers a complete overview of the vulnerability panorama for the third quarter of 2023, breaking down vulnerabilities by vendor and product, in addition to presenting a severity diagram that highlights vulnerabilities based mostly on exploitability and the provision of options.
(Picture supply: https://flashpoint.io/weblog/cyber-threat-intelligence-index-q3-2023/)
General Vulnerability Statistics for Q3 2023:
- 7,373 vulnerabilities have been disclosed.
- 1,167 vulnerabilities have been disclosed with out a CVE ID.
- 12 months-to-date (YTD), there have been 23,268 vulnerabilities.
- 2,752 of those vulnerabilities are categorized as excessive or vital, based mostly on the CVSSv2 ranking system.
Vulnerabilities by Vendor:
- Canonical leads with near 500 vulnerabilities.
- Microsoft Company follows with simply over 400 vulnerabilities.
- SUSE has barely fewer than 400 vulnerabilities.
- Google and Dell have fewer than 300 vulnerabilities, with Dell having the least among the many listed distributors.
Vulnerabilities by Product:
- Ubuntu has the best variety of vulnerabilities, near 500.
- Debian Linux stands subsequent with slightly over 400 vulnerabilities.
- Merchandise like OpenSUSE Leap, SUSE Linux Enterprise Server, and SUSE Linux Enterprise Excessive Efficiency Computing every have vulnerabilities numbering between 100 and 300, with OpenSUSE Leap exhibiting the best among the many three.
Actionable Severity Diagram:
- 2,403 vulnerabilities include a public exploit.
- 4,223 vulnerabilities are remotely exploitable.
- 5,228 vulnerabilities have an answer obtainable.
- A subset of 826 vulnerabilities are distinctive in that they possess all three attributes: they’ve a public exploit, are remotely exploitable, and have an answer obtainable.
Malware IOCs Quickview
This graphic affords an in depth view of the malware panorama for the third quarter of 2023. It outlines the dominant malware households and kinds, and likewise breaks down prevalent cyber-attack techniques and strategies in line with the MITRE ATT&CK framework. The information emphasizes the continuing risk of CobaltStrike as a malware household, the continual prominence of Trojans, and the numerous use of command and management techniques by cyber adversaries.
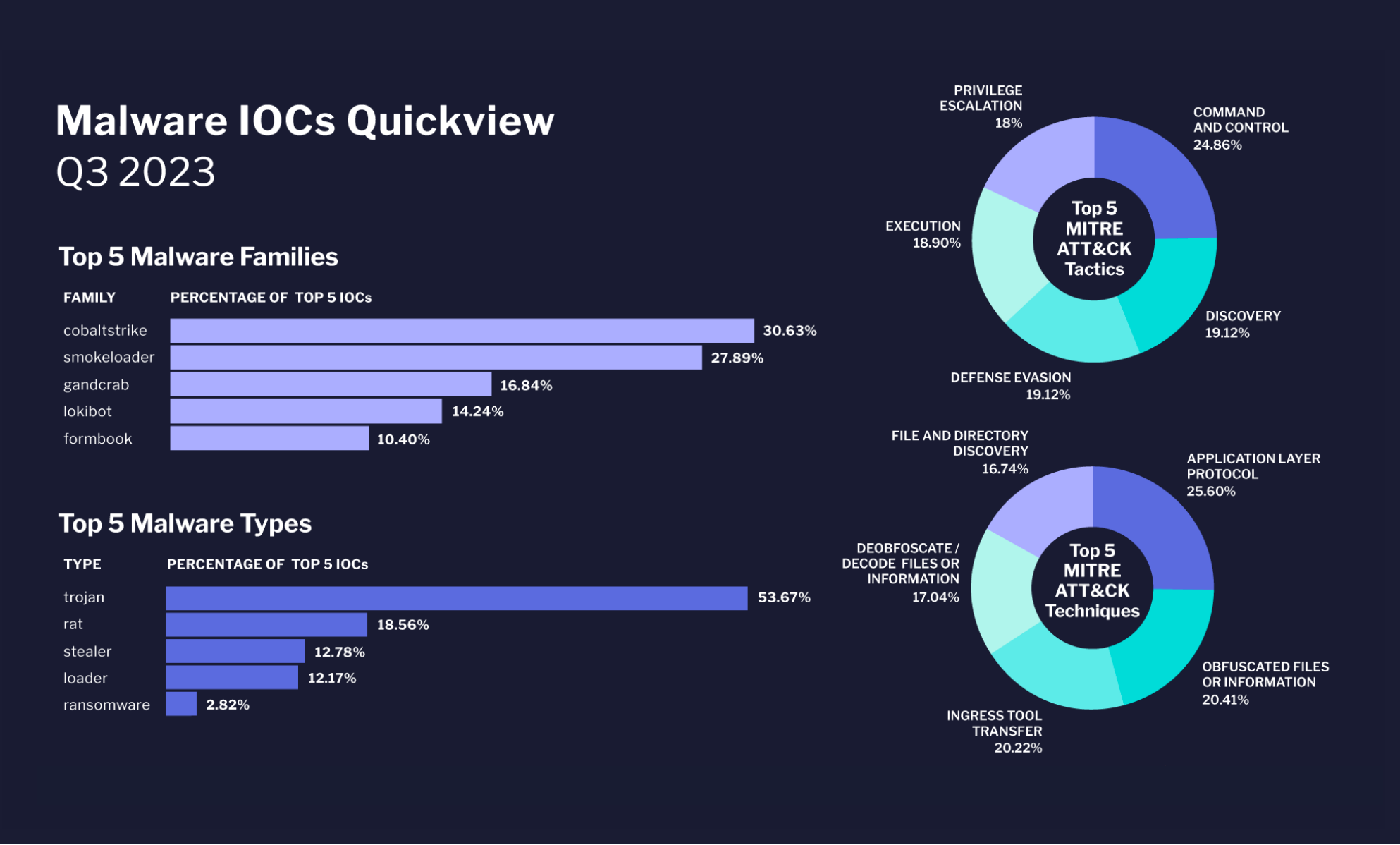
High 5 Malware Households:
- CobaltStrike takes the lead, representing 30.63% of the highest 5 Indicators of Compromise (IOCs).
- SmokeLoader follows at 27.89%.
- GandCrab is at 16.84%.
- Lokibot constitutes 14.24%.
- Formbook trails at 10.40%.
High 5 Malware Varieties:
- Trojans are essentially the most prevalent, accounting for 18.56% of the highest 5 IOCs.
- RAT (Distant Entry Trojan) comes subsequent at 18.56%.
- Stealer sort malware constitutes 12.78%.
- Loader represents 12.17%.
- Ransomware, whereas notorious, solely accounts for 2.82% of the highest 5 IOCs.
High 5 MITRE ATT&CK Techniques:
- Command and Management is the predominant tactic at 24.86%.
- Utility Layer Protocol is an in depth second at 25.60%.
- Discovery and Protection Evasion each maintain equal proportions at 19.12% every.
- Execution is noticed at 18.90%.
- Privilege Escalation accounts for 18%.
- File and Listing Discovery is at 16.74%.
High 5 MITRE ATT&CK Strategies:
- A considerable 53.67% of the strategies contain Deobfuscating/Decoding recordsdata or info.
- Obfuscated Recordsdata or Data strategies account for 20.41%.
- Ingress Software Switch stands at 20.22%.
As we transfer into 2024, the risk posed by malware and safety breaches stays ever-present and ever-evolving. In mild of this, it’s important for people and organizations alike to proactively arm themselves in opposition to such threats. Listed below are key measures to make sure safety in opposition to the multifaceted panorama of cyber threats:
- Training and Consciousness: Information is the primary line of protection. Keep knowledgeable concerning the newest threats and familiarize your self with widespread phishing techniques. Commonly conducting cybersecurity coaching classes can considerably cut back the probabilities of an inadvertent breach.
- Common Software program Updates: Be certain that all working methods, functions, and antivirus software program are up-to-date. Cyber attackers typically exploit identified vulnerabilities in outdated software program.
- Multi-Issue Authentication (MFA): Implement MFA wherever attainable. This provides a further layer of safety, making it considerably more difficult for attackers to achieve unauthorized entry.
- Backup Commonly: Keep common backups of important information, saved each domestically and within the cloud. This ensures information availability, even when hit by ransomware or different harmful malware.
- Firewalls and Antimalware Instruments: Make use of a strong firewall to observe and management incoming and outgoing community site visitors. Couple this with a good antimalware answer to scan, detect, and take away threats.
- Restrict Entry: Use the precept of least privilege (PoLP). Be certain that customers and functions solely have the entry essential to carry out their duties, decreasing the potential harm of a breach.
- Safe Bodily Entry: Not all breaches are digital. Be certain that delicate areas and methods are secured bodily in opposition to unauthorized entry.
- Common Audits and Penetration Testing: Periodically assess the group’s cybersecurity posture. Common penetration testing can establish vulnerabilities earlier than attackers do.
- Keep Up to date with Patches: Distributors typically launch patches for identified vulnerabilities. Making use of these patches in a well timed method is essential.
- Community Segmentation: By segmenting the community, an an infection or breach in a single phase will be contained, stopping it from spreading to different components of the group.
In conclusion, the strategy to cybersecurity as we advance into 2024 should be holistic, encompassing expertise, processes, and other people. By fostering a tradition of safety consciousness, mixed with the implementation of superior protecting measures, we are able to navigate the digital age with higher confidence and resilience in opposition to the rising tide of cyber threats.
By Randy Ferguson
[ad_2]