[ad_1]
Examine traits
We recognized 2793 research from the databases, which we then screened primarily based on our inclusion and exclusion standards. As proven in Fig. 1 and 28 research [17, 21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47] finally met our standards and have been included on this evaluation. Particulars of those research are offered in Desk 1. All research have been carried out utilizing rats (n = 19) and mice (n = 9). Other than two research that utilized photochemistry and electrocoagulation methods, the prevalent method was the suture technique of center cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) (n = 26). Mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) have been the first supply of EVs in most research (n = 15), with different sources together with neural stem cells (NSC) (n = 5), blood (n = 5), and soma (n = 3). The predominant technique of engineering EVs was by way of lentiviral transfection (n = 16), adopted by coculture (n = 7), ultrasonic methods (n = 3), electroporation (n = 1), and floor modification (n = 1). The popular route of EEVs administration was intravenous injection (n = 21), although some research opted for intracerebral injection (n = 5) or nasal administration (n = 2). Administration timing different, spanning from a day earlier than IS (n = 2) to 14 days post-IS (n = 26), with choose research administering EVs on a number of events (n = 5). Notably, a good portion of research engineered the dad or mum cells (n = 19), versus immediately engineering the EVs (n = 9).
Outcomes
EEVs scale back infarct quantity and enhance neurological scores after IS
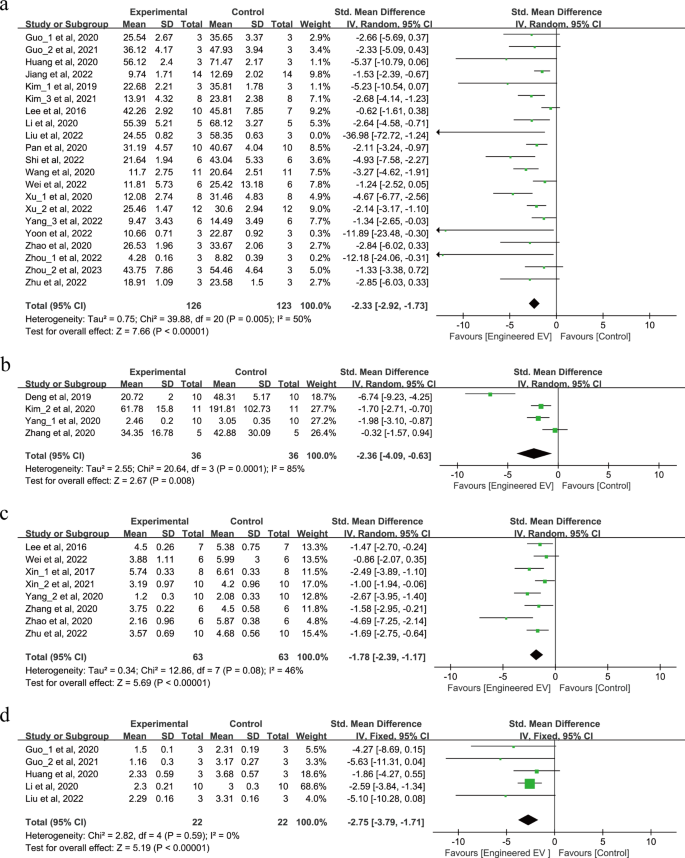
The consequences of EEVs remedy on infarct quantity and neurological scores have been proven in Fig. 2a-d. A complete of 321 animals in 25 research reported adjustments in infarct quantity after remedy with EEVs, of which 21 research reported the proportion of infarct quantity (Fig. 2a) and 4 research reported the dimensions of infarct quantity (Fig. 2b). The outcomes confirmed that the EEVs lowered the proportion of infarct quantity (SMD = -2.33, 95% CI: -2.92, -1.73, p < 0.00001, Tau2 = 0.75, I2 = 50%) and the dimensions of infarct quantity (SMD = -2.36, 95% CI: -4.09, -0.63, p = 0.008, Tau2 = 2.55, I2 = 85%) in comparison with pure EVs remedy.
Moreover, we examined the impact of EEVs remedy on neurological scores after IS. In 8 research, 126 animals have been assessed utilizing the modified neurological severity rating (mNSS) (Fig. 2c), and 44 animals in 5 research used the Zea-Longa rating (Fig. 2d). The outcomes confirmed that remedy with EEVs considerably improved mNSS after IS (SMD = -1.78, 95% CI: -2.39, -1.17, p < 0.00001, Tau2 = 0.34, I2 = 46%). Equally, the Zea-Longa rating demonstrated comparable outcomes (SMD = -2.75, 95% CI: -3.79, -1.71, p < 0.00001, I2 = 0%).
EEVs promote behavioral restoration after IS
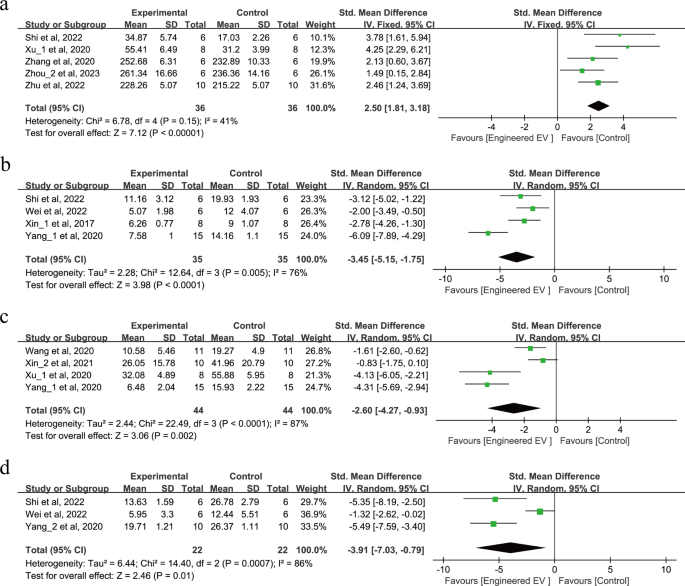
Behavioral assessments have been carried out on a complete of 274 animals throughout 11 research as proven in Fig. 3a-d. For motor and coordination operate, 5 research carried out the rotarod check (SMD = 2.50, 95% CI: 1.81, 3.18, p < 0.00001, I2 = 41%) as proven in Fig. 3a, whereas 4 research carried out the grid-walking check (SMD = -3.45, 95% CI: -5.15, -1.75, p < 0.0001, Tau2 = 2.28, I2 = 76%) as proven in Fig. 3b. For motor and sensory operate, 4 research carried out adhesive elimination check (SMD = -2.60, 95% CI: -4.27, -0.93, p = 0.002, Tau2 = 2.44, I2 = 87%) as proven in Fig. 3c. For studying and reminiscence operate, 3 research carried out the morris water maze check (SMD = -3.91, 95% CI: -7.03, -0.79, p = 0.01, Tau2 = 6.44, I2 = 86%) as proven in Fig. 3d. In abstract, all these assessments recommend that remedy with EEVs improves behavioral restoration after IS.
EEVs scale back the discharge of pro-inflammatory components after IS
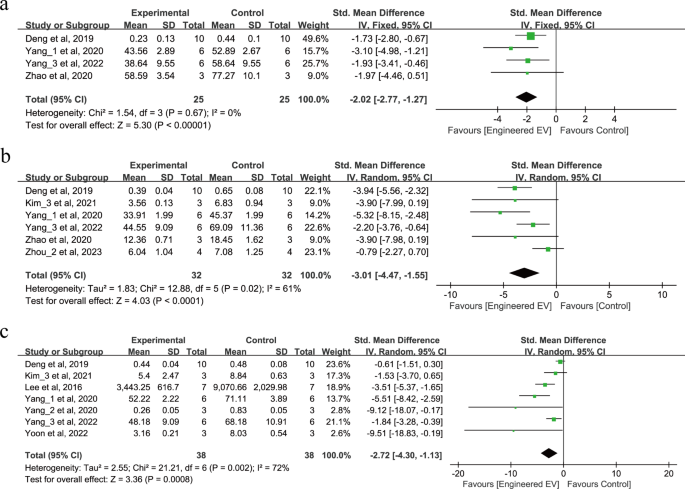
9 research involving 190 animals reported the discharge of pro-inflammatory components after IS as proven in Fig. 4a-c. 4 research reported that EEVs can scale back IL-1β (SMD = -2.02, 95% CI: -2.77, -1.27, p < 0.00001, I2 = 0%) as proven in Fig. 4a. 6 research reported that EEVs can scale back the discharge of IL-6 (SMD = -3.01, 95% CI: -4.47, -1.55, p < 0.0001, Tau2 = 1.83, I2 = 61%) as proven in Fig. 4b. 7 research reported that EEVs can even scale back the discharge of TNF-α (SMD = -2.72, 95% CI: -4.30, -1.13, p = 0.0008, Tau2 = 2.55, I2 = 72%) as proven in Fig. 4c. In abstract, these research all show that remedy with EEVs can scale back the discharge of pro-inflammatory components after IS.
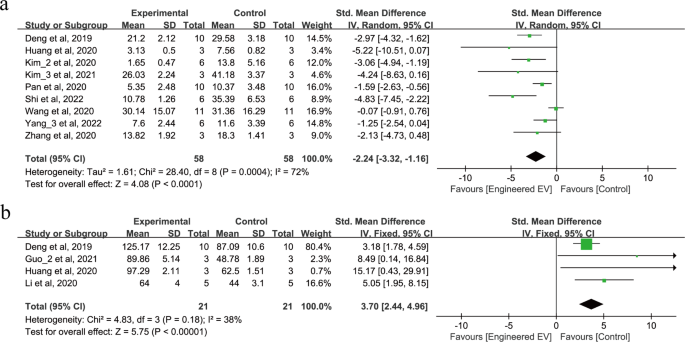
EEVs scale back apoptosis fee and improve the variety of neurons after IS
11 research involving 158 animals reported on the apoptosis fee and the variety of neurons after IS, as proven in Fig. 5a-b. 9 research reported that remedy with EEVs scale back apoptosis fee (SMD = -2.24, 95% CI: -3.32, -1.16, p < 0.0001, Tau2 = 1.61, I2 = 72%) as proven in Fig. 5a. 4 research reported that remedy with EEVs considerably improve neuron numbers after IS (SMD = 3.70, 95% CI: 2.44, 4.96, p < 0.00001, I2 = 38%) as proven in Fig. 5b.
Subgroup and sensitivity analyses
We carried out a subgroup evaluation to discover the supply of heterogeneity. As proven in Desk 2, we didn’t observe vital sources of heterogeneity within the final result of infarct quantity amongst subgroups of randomization, blinding, animal species, supply of EVs, strategies of engineering, engineering targets, route of administration, and the timepoint of administration. We additionally carried out a sensitivity evaluation to make sure the robustness of figuring out the general impact measurement of the noticed final result measurements. We eliminated one research at a time and recalculated the pooled impact measurement for the remaining research. The outcomes confirmed that for all outcomes, there was no vital enchancment in heterogeneity between research, indicating that no research had pushed the supply of heterogeneity.
Analysis high quality and bias threat
As proven in Desk 3, the median high quality evaluation rating for the research was 7 factors (IQR: 6–9). Nevertheless, most research employed the precept of random allocation and just a few reported concealment of allocation. Half of the research used a blinding to judge the outcomes. Just one research offered info on pattern measurement calculation, which acquired a threat of bias rating of 10 factors, as proven in Desk 4.
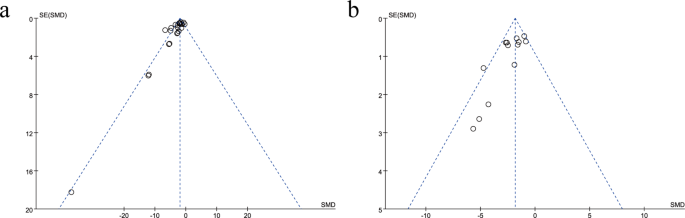
Publication bias
We additionally carried out a publication bias check and generated funnel plots for final result measures that included greater than ten research. The outcomes indicated publication bias for each of our final result measures. The funnel plots for infarct quantity and neurological scores appeared asymmetrical, as illustrated in Fig. 6, with a majority of the research indicating extra constructive results of EEVs.
[ad_2]