[ad_1]
Supplies
Riv was bought from Shanghai Yuanye Biotechnology Co., Ltd. Pyrrole, thrombin, prostaglandin 1 (PGE1) and protease inhibitor (PMSF) had been bought from Shanghai Maclean Biochemical Know-how Co., Ltd. Ferric chloride hexahydrate, ammonium persulfate, sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS), calcium chloride had been bought from Tianjin Hengxing Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. 1,1′-dioctadecyl-3,3,3′,3′-tetramethylindodicarbocyanine, 4-chlorobenzenesulfonate salt dye (DiD dye), Calcein-AM dye, phosphate buffered saline (PBS) and fetal bovine serum (FBS) had been bought from Meron Biotechnology Co.,Ltd. The used water was deionized water and all experimental chemical compounds had been of reagent grade. All animal experiments had been authorised by the Animal Heart of Shenyang Pharmaceutical College. Sprague-Dawley rats (SD rats) (180–220 g, males) and Kunming mice (KM mice) (18–22 g, males) had been from ChangSheng Biotechnology Firm Restricted (Liaoning, China), which had been raised in SPF atmosphere.
Preparation of NPs
In accordance with a beforehand reported methodology for rat platelet purification, the orbited entire blood of SD rats was collected into the gathering vessels containing anticoagulants by capillary methodology. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) was obtained by centrifugation at 200 g for 10 min at room temperature. An equal quantity of ACD answer (acid-citrate-dextrose) was added and centrifuged at 100 g for 10 min to take away the remaining erythrocytes [15]. After centrifugation at 800 g for 10 min, the supernatant was discarded and the platelets had been resuspended in PBS containing 2 μM PGE1 and PMSF. These had been repeated freeze-thaw cycles for thrice, centrifuged at 4000 rpm for 4 min, and washed thrice with PBS containing PMSF. Lastly, the platelet membranes had been resuspended in 0.2 mM EDTA aqueous answer and saved at -80℃ for additional use.
0.3 g of SDS was weighed and dissolved in 5 mL of deionized water, and 75 μL of pyrrole monomer and about 4 mg of Riv had been added. The answer was stirred to dissolve utterly, after which 0.0492 g of ammonium persulfate was added to oxidize and polymerize for two h to type SDS-PPy/Riv NPs. Subsequently, the obtained platelet membranes had been co-sonicated with NPs in an ice bathtub for 20 min after which the extruder of 200 nm polycarbonate membrane was used to extruder 10 instances to take away the surplus platelet membrane to acquire PLT-PPy/Riv NPs with uniform particle dimension. The PLT-PPy NPs had been ready as above with out the addition of Riv.
Characterization of nano-formulations
The scale, polydispersity index, and zeta potential of SDS-PPy/Riv NPs and PLT-PPy/Riv NPs had been measured by Zetasizer. The morphological modifications of nanoformulations (SDS-PPy/Riv NPs and PLT-PPy/Riv NPs) had been characterised by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) after destructive staining with sodium phosphotungstic acid answer. We used an ultrafiltration methodology to research the leakage of Riv from nano-formulations in a physiological atmosphere to guage the steadiness of the NPs in vitro. In accordance with a earlier report, the composition of FBS was similar to that of physique fluids [21], and PBS (pH 7.4) containing 10% FBS was usually utilized in stability experiments to simulate the medium of the physiological atmosphere [22]. Briefly, we incubated PLT-PPy/Riv NPs in PBS (pH 7.4) containing 10% FBS for 12 h at 37 ℃. The samples had been positioned in ultrafiltration tube with a cut-off molecular weight of 30 kDa, and centrifuged (4000 rpm, 10 min), and the focus of Riv within the filtrate was decided by HPLC at pre-set time intervals. Lastly, with a view to discover the motion mechanism of the core polymer, we used Chemdraw and Supplies studio to conduct molecular docking and display the diploma of pyrrole polymerization on the optimum binding vitality of PPy and Riv.
In vitro light-triggered Riv launch
The discharge habits of Riv in PLT-PPy/Riv NPs was decided by dialysis methodology. PBS (pH = 7.4) containing 0.2% SDS was used as the discharge medium. The ready NPs had been positioned within the dialysis bag with a molecular weight of 3500 Da and immersed in 100 mL of launch medium. The laser irradiation group was irradiated with 808 nm (2.22 W/cm2) laser for 10 min earlier than the discharge, and subsequently 2 mL pattern was taken at predetermined time to find out the focus of Riv by HPLC whereas supplementing an equal quantity of the discharge medium answer. After which the cumulative launch quantity of Riv was calculated.
In vitro photothermal efficiency of PLT-PPy/Riv NPs
PCE
To analyze the photothermal efficiency of the ready formulations, PBS, SDS-PPy/Riv NPs, PLT-PPy NPs, and PLT-PPy/Riv NPs had been irradiated with 808 nm laser respectively. The temperature modifications and thermal imaging maps of various samples had been recorded by infrared thermal imager throughout laser illumination. When the samples had been discovered to heat as much as a secure stage, the irradiation was stopped. In the meantime, with a view to calculate the PCE of PLT-PPy/Riv NPs, we recorded the cooling change and fitted the cooling curve. The amount of every experiment was 1 mL. The calculation formulation of the PCE of PLT-PPy/Riv NPs is as follows [23]:
$$eta = frac{{hsDelta Tmax – Qs}}{{I(1 – {{10}^{ – A}})}}$$
$$theta =frac{T-Tsur}{Tmax-Tsur}$$
$${rm{t = – tau Intheta }}$$
Within the equation, s is the floor space. h is the warmth switch coefficient. Tmax is the utmost temperature at equilibrium. Tsur is the ambient temperature. Qs is the warmth absorption charge of water. I is the laser energy density. A is the absorbance of the NPs at 808 nm, and τ is the time fixed.
Photothermal stability
To judge the photothermal stability of PLT-PPy/Riv NPs, 1 mL PBS answer, Riv Sol, SDS-PPy/Riv NPs, PLT-PPy NPs and PLT-PPy/Riv NPs had been respectively irradiated underneath 808 nm (2.2 W ·cm-2) laser for 10 min. The laser was turned off and cooled naturally. The cooling modifications of PLT-PPy/Riv NPs over time had been recorded and repeated 3 instances.
Evaluation of goal means in vitro
In vitro research of activated platelet focusing on means
We diluted the DiD inventory answer into the DiD working answer and incubated it with the obtained platelet membranes at 37 ℃ for 20 min. After incubation, the answer was centrifuged at 800 g for 3 min and washed repeatedly for a number of instances to take away the surplus DiD. Lastly, the DiD-labeled cell membranes had been resuspended with PMSF-containing PBS answer for standby. The DiD-labeled NPs had been obtained by sonicating the DiD-labeled cell membranes with SDS-PPy/Riv NPs for 20 min and washing them a number of instances by centrifugation in PBS. The DiD-labeled NPs had been incubated with the extracted inactivated platelets (dissolved in PBS answer containing 30 ng/mL (PGE1) and activated platelets (dissolved in PBS answer containing 8 × 10− 9 M CaCl2 and a pair of U/mL thrombin) for 30 min [16]. Then the answer was washed repeatedly with PBS to take away the free NPs, and the DiD-labeled NPs had been resuspended in PBS for evaluation by circulation cytometry.
To additional confirm the adhesion of PLT-PPy/Riv NPs to activated platelets, confocal microscopy was used for visible evaluation. Platelets extracted from contemporary blood of rats (activated and inactivated teams) had been labeled with Calcein-AM, after which co-incubated with DiD-labeled NPs for 45 min. And after the tip of co-incubated, the platelets had been washed thrice by centrifugation at 250 g. Lastly, they had been resuspended with PBS answer, filmed, and noticed by confocal statement.
In vitro focusing on means of clots
So as to additional consider the in vitro focusing on means of the ready formulations, we explored the focusing on means of PLT-coated NPs to the ready synthetic blood clots. Contemporary entire blood of rats was collected by capillary orbital-blood extraction in microcentrifuge tubes with a closing focus of 1 U·mL− 1 thrombin and a pair of.5 mM CaCl2 answer, which was incubated at 37℃ for 1 h to acquire the softer synthetic blood clots [12]. PBS, Riv answer (Riv Sol), SDS-PPy/Riv NPs, PLT-PPy NPs, and PLT-PPy/Riv NPs had been incubated with synthetic blood clots for 30 min, respectively, and the surplus NPs had been eliminated by washing with PBS. Lastly, the fluorescence depth was detected with in vivo imaging system (IVIS).
In vitro thrombolysis research
Right here, we used the Drabkin methodology to evaluate the in vitro thrombolytic impact of various preparations. Then the in vitro antithrombotic check was carried out, and the above-prepared clots had been randomly divided into 5 teams. After laser remedy with PBS, Riv Sol, SDS-PPy/Riv NPs, PLT-PPy NPs and PLT-PPy/Riv NPs (all of the administration teams obtained equal doses of 0.9 mg/kg Riv), respectively, the equal quantity of Drabkin’s reagent was added and positioned at room temperature for 20 min. After centrifugation at 10,000 g for 10 min, the supernatant was taken and the OD worth of cyanogenic hemoglobin was decided at 540 nm through the use of a microplate reader.
Evaluation of thrombolysis in vivo
Mouse thrombosis mannequin and antithrombic impact
SD rats had been anesthetized by intraperitoneal injection of chloral hydrate (10%). After the rats had been supine and secured with tape, the fur was eliminated through the use of depilatory cream and an incision was made within the inside thigh to reveal the femoral vessels. Then the femoral vessels had been lined with filter paper (0.5 cm × 0.5 cm) saturated with 10% ferric chloride answer for five min to type femoral thrombosis. Residual ferric chloride was then eliminated by rinsing with saline. We randomly divided the SD rats of the thrombosis mannequin into 5 teams: PBS group (management group), Riv Sol group (drug-only group), SDS-PPy/Riv NPs + laser group (photothermal + drug remedy group), PLT-PPy NPs + laser group (photothermal group solely), PLT-PPy/Riv NPs + laser group (photothermal + drug-targeted remedy group) (all of the drug-treated rats obtained an equal dose of 0.9 mg/Kg Riv). Within the laser group, 808 nm laser irradiation was carried out for 10 min after 75 min of tail vein injection, adopted by wound suturing. After 24 h, the thrombus-containing femoral vessels had been eliminated and immersed in 4% paraformaldehyde, then had been embedded, sectioned, stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E), and noticed through the use of mild microscopy. Lastly, the thrombus clearance space was calculated quantitatively through the use of picture J. The thrombus clearance charge is calculated as follows:
$${rm{Thrombus}},{rm{clearance}},{rm{charge = }},{rm{Delta }}{{rm{W}}_{rm{0}}}{rm{/W instances 100% }}$$
∆W0 is the world of thrombus clearance and W is the world of the vessel lumen.
In vivo imaging
The FeCl3-induced formation of rat femoral thrombosis mannequin was established through the use of the identical methodology as above. So as to display the optimum laser irradiation time after intravenous administration in rats, we injected DiD-labeled PLT-PPy/Riv NPs within the tail vein. In vivo imaging system (IVIS) was carried out at intervals of 15, 30, 45, 60, 75, and 90 min, respectively, and the fluorescence depth was recorded, and the time of most fluorescence depth was taken as the beginning time of laser irradiation.
Additionally, to research the photothermal effectivity of PBS, SDS-PPy/Riv NPs, PLT-PPy NPs, and PLT-PPy/Riv NPs, the rat femoral vessels had been uncovered to laser (808 nm, 2.22 W/cm2) for 10 min at 75 min after administration. The infrared thermal photographs and native temperature modifications had been recorded by infrared thermal imaging digital camera.
Tail bleeding and clotting time evaluation
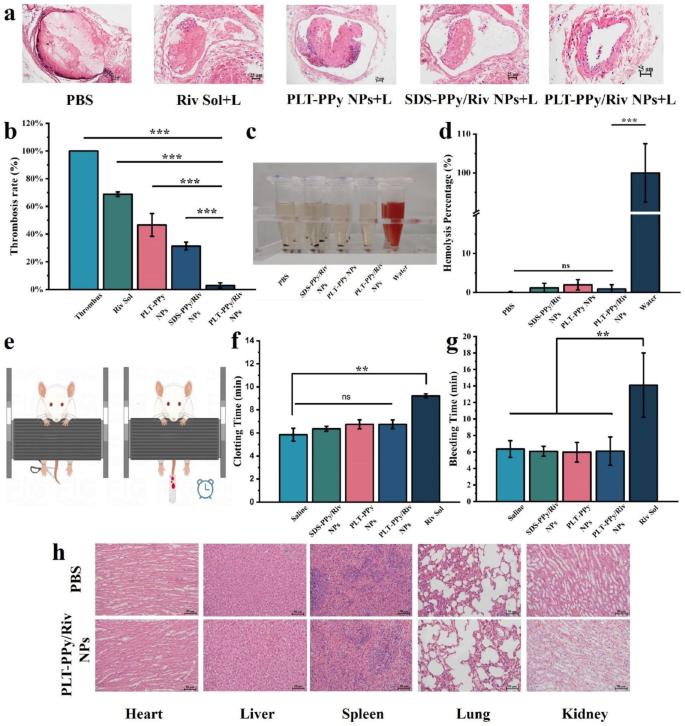
After anesthesia with intraperitoneal injection of chloral hydrate (7%), KM mice had been injected intravenously with PBS, Riv Sol, SDS-PPy/Riv NPs, PLT-PPy NPs, and PLT-PPy/Riv NPs. After 4 h of administration, the distal finish of the tail (1 cm) of mice was reduce with surgical scissors (Fig. 2e). Tail bleeding time and clotting time had been recorded to guage the anticoagulant impact. Bleeding time was outlined because the time required to cease bleeding from the wound for not less than 10 s [24]. The clotting time was measured via the glass slide methodology by taking 50 μL of the entire blood on a dry slide and beginning the timing till the looks of fibrin filaments [25].
Analysis of site-specific photothermal-amplified thrombolytic impact and security of PLT-PPy/Riv NPs in FeCl3-induced rats fashions of LEDVT. a Histological microscopic evaluation of rat vessels after remedy with completely different formulations. Scale bar = 25 μm. b Quantification of thrombus clearance by the ratio of thrombolytic space/whole lumen space (n = 3). c Qualitative and quantitative d evaluation of the hemolysis exercise of SDS-PPy/Riv NPs, PLT-PPy NPs, and PLT-PPy/Riv NPs on the similar Riv focus (n = 3). e The mice tail-cutting mannequin for tail bleeding check. f The clotting time and g bleeding time within the tail bleeding check (n = 3). h The H&E sections of coronary heart, liver, spleen, lung and kidney of PBS and PLT-PPy/Riv NPs remedy group for evaluating the histopathological modifications. Scale bar = 25 μm. Statistical evaluation was by way of one-way ANOVA with GraphPad Prism 8.0; ns: no significance, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001
Analysis of therapeutic security
To preliminarily assess the toxicity of the ready preparations, the hemolysis charge of purple blood cells (RBCs) in SD rats was decided. The collected blood of 1 mL of SD rats was positioned in an anticoagulant tube and centrifuged on the pace of 8000 rpm for five min to acquire erythrocyte precipitates. 1 mL of PBS was added and the erythrocytes had been washed and centrifuged a number of instances till the supernatant was clarified. Then, the lyophilized PLT-PPy NPs, PLT-PPy/Riv NPs and SDS-PPy/Riv NPs had been dissolved in PBS containing erythrocytes because the experimental group. The optimistic and destructive management group had been deionized water and PBS, respectively. After co-culture at 37 ℃ for 4 h, the combination was centrifuged at 13,000 rpm for 10 min to take away the unbroken erythrocytes. The supernatant was taken in a 96-well plate, and the absorbance at 540 nm was measured with a microplate reader.
Along with thrombus-containing vessels, the organs (coronary heart, liver, spleen, lung, kidney) of various teams had been took in flip, immersed in 4% paraformaldehyde, embedded, sectioned, stained with H&E and the pathological modifications had been noticed by mild microscopy.
Statistical evaluation
All knowledge on this experiment had been offered as imply ± commonplace deviation (SD). One-way evaluation of variance (ANOVA) was carried out through the use of GraphPad Prism to find out statistical significance. The asterisks denote the extent of statistical significance (ns: no significance, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 and ****p < 0.0001).
[ad_2]